#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int ChildProcess(void);
int ParentProcess(void);
int pid;
int i,len;
int parent_pid;
int child_pid;
int the_pid;
int pipe_read=0,pipe_write=1;
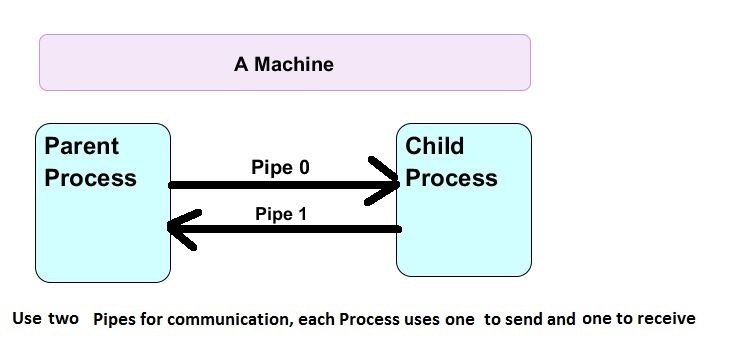
int p_parent[2],p_child[2];
int main(void){
pipe(p_parent);
pipe(p_child);
parent_pid=getpid();
child_pid=fork(); /*Returns child_pid to parent*/
if (getpid()==parent_pid) {
ParentProcess();
} else {
ChildProcess();
}
return 0;
}
int ChildProcess(void)
{
char parent_said[5];
close(p_child[pipe_read]);
close(p_parent[pipe_write]);
while (i<2) {
len=read(p_parent[pipe_read], parent_said, 1024);
printf(" parent just wrote %s\n",parent_said);
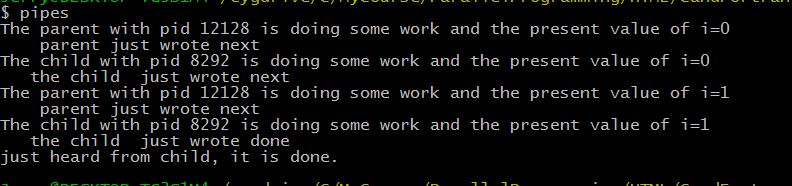
printf ("The child with pid %d is doing some work and the present value of i=%d\n", getpid(),i);
i++;
if (i==2) {
write(p_child[pipe_write], "done", 5);
sleep(3);
break;
}
write(p_child[pipe_write], "next", 5);
sleep(3);
}
return 0;
}
int ParentProcess(void){
char child_said[5];
close(p_child[pipe_write]);
close(p_parent[pipe_read]);
while (i<2) {
printf ("The parent with pid %d is doing some work and the present value of i=%d\n", getpid(),i);
write(p_parent[pipe_write],"next", 5);
i++;
sleep(1);
len=read(p_child[pipe_read], child_said, 1024);
printf(" the child just wrote %s\n",child_said);
}
len=read(p_child[pipe_read], &child_said, 1024);
printf("just heard from child, it is %s.\n",child_said);
return 0;
}
Note: There is an assumption that after the fork the parent is before the child in the queue.

