(See: Drugs in American Society, 5th, 6th, and 7th editions, Erich Goode, McGraw-Hill, 1999-2008. Chapters 14 and 15)
![]()

(or should that be "No thanks, I can make up my own mind?")
![]()
![]()

![]()
Widespread today, practically universal
 Early
approaches: Cognitive
Early
approaches: Cognitive  Late
1970's: Affective Education/Values Clarification.
Late
1970's: Affective Education/Values Clarification.  1980's
and into the 21st Centruy- Social Inoculation
1980's
and into the 21st Centruy- Social Inoculation
- Safety First Web Site
- Teenagers can make responsible decisions if given honest information.
- Accept reality of experimentation: Focus on safe outcomes,
- Drugs are Drugs--legal and otherwise. Good and Bad are normative issues, not inherent properties of substances.
- Abstinence may not be realistic goal for all.
- Controlled use is the norm and a practical goal.
- Promote stake in life and responsible lifestyles: Build individuals not defenses
- Promoting rational thought and objective analysis will be of benefit to the entire educational process.
Studies:
- " Safety First: A Reality-Based Approach to Teens, Drugs, and Drug Education," (.pdf file) Marsha Rosenbaum (TLC)
- Safety First: Parent, Teens, and Drugs, Marsha Rosenbaum (Drug Policy Alliance).
- Assessing the Effects if School-Based Drug Education, by Dennis P. Rosenbaum, Ph.D. Professor and Head and Gordon S. Hanson, Ph.D. Research Associate Department of Criminal Justice and Center for Research in Law and Justice University of Illinois at Chicago, April 6, 1998.
- Scare tatics don't work.
![]()
![]()
 Treatment
Theories
Treatment
Theories![]() Learning/Free
will: Value issue, choices, decision making: Education
Learning/Free
will: Value issue, choices, decision making: Education
![]() Moral
Model: Immoral choice- Punish. Prison.
Moral
Model: Immoral choice- Punish. Prison.
![]()
![]()
 Studies on Treatment
Studies on Treatment ![]()
 General Considerations
General Considerations ![]()
 Criteria for Evaluation
Criteria for Evaluation ![]()
![]()

![]()
- Accuracy
- False positives and False Negatives
- Type of test: Urine- cheap varieties (even dip sticks) $15-30. High error rates. State of the art: Gas Chromography/Mass Spectrometry (machine cost $15,000), test $100 or more: Fairly reliable. Hair test: still being evaluated by scientific community- popular within the private sector
- Issue: Previous use or intoxication (presence of metabolites)
- Problems: Other substance interaction and security.
- Overall (for urine tests) 2% false positives, 30% false negatives.
- Hair Testing: level of dectection? Dark hair versus light hair? African-American versus Caucasians, impact of bleaching, etc., and environmental contamination.
- Use versus Abuse: What are we testing for?
- Usefulness: Lower number of positives correlated with deterrence or overall lower use levels?
- Firms with drug testing: Lower productivity (issue of trust, degrading experience, deters qualified employees).
- Drug users are not necessarily less reliable, nor unsafe.
- Cost effectiveness: Federal program--spent $11.7 Million (29,000 tests). 153 positives (.5%). This equals $77,000 per positive.
![]()
![]()

![]()
| 1906 | Pure Food and Drug Act | Regulates food production,"The Jungle," clamps down on misrepresentation, institutes content labeling, decline of "patent medicines," Beginning of government regulation |
| 1912 | Sherly Amendment | Focus on effectiveness |
| 1914 | Harrison Narcotics Act | Regulates Production, Importation, Distribution, and Use of Opiates. Department od treasury: Narcotics Division established |
| 1922 | Narcotic Drug Import and Export Act (Jones -Miller Act) | Intended to eliminate use of narcotics except for legitimate medicinal use. Establishes: Federal Narcotics Control Board (Still Treasury Department) |
| 1924 | Heroin Act | Makes it illegal to manufacture heroin |
| 1929 | Focus shift to curing addiction (Linder Case 1925) | Federal Hospitals in Lexington and Fort Worth for Narcotic Addiction |
| 1930 | Issue of Corruption in Narcotics Board | Bureau of Narcotics (Harry Anslinger) |
| 1937 | Marijuana Tax Act | Applies controls over marijuana similar to narcotics |
| 1938 | Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act | FDA given control over drug safety, Drugs redefined:effect body even in absence of disease, Establishes class of drugs available by Prescription (Company determines status) |
| 1942 | Opium Poppy Control Act | Prohibits growing poppy w/o license |
| 1951 | Durham-Humphrey Amendment | Established more specific guidelines for prescription drugs: habit forming, safety, and evaluation of new drugs |
| 1951 | Boggs Amendment to the Harrison Narcotic Act | Mandatory sentences for narcotic violations |
| 1956 | Narcotics Control Act | Intends to impose even more severe penalties for narcotics violations |
| 1965 | Drug Abuse Control Amendments (DACA) | Strict controls over amphetamines, barbiturates, LSD, etc. (Bureau of Narcotics and dangerous Drugs) |
| 1966 | Narcotic Addict Rehabilitation Act (NARA) | Allows treatment as an alternative to jail |
| 1968 | DACA Amendments | Provides that sentence may be suspended and record expunged if no further violations within 1 year |
| 1970 | Comprehensive Drug Abuse and Control Act | Replaces and updates all previous laws concerning narcotics and other dangerous drugs. Emphasis on law enforcement. |
| 1972 | Drug Abuse Office and Treatment Act | Establishes federally funded programs for prevention and treatment |
| 1973 | Methadone Control Act | Regulates methadone licensing |
| 1973 | Heroin Trafficking Act | Increases penalties for distribution |
| 1973 | Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration (ADAMHA) | Consolidates NIMH, NIDA, and NIAAA under umbrella organization |
| 1973 | Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) | Remodels Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs into DEA |
| 1974 and 1978 | Drug Abuse Treatment and Control Amendments | Extends 1972 act |
| 1978 | Alcohol and Drug Abuse Education Amendments | Sets up education programs within Department of Education |
| 1980 | Drug Abuse Prevention, Treatment, and Rehabilitation Amendments | Extends prevention education and treatment programs |
| 1984 | Drug Offenders Act | Sets up special programs for offenders and organizes treatment |
| 1986 | Analogue (Designer Drug) Act | Makes use of substances with similar effects and structure to existing illicit drug illegal |
| 1988 | Anti-Drug Abuse Act | Establishes oversight office: National Drug Control Policy |
| 1992 | ADAMHA Reorganization | Transfers NIDA, NIMH, and NIAAA to NIH and incorporates ADAMHA's programs into the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) |
![]()
Fiscal Year |
Total |
||||
Inflation - Adjusted Dollars in Millions (base year = 1998) |
|||||
1981 |
2,747.0 |
745.3 |
788.3 |
292.1 |
921.3 |
1982 |
2,903.4 |
802.8 |
965.2 |
281.4 |
854.0 |
1983 |
3,268.4 |
1,084.9 |
960.0 |
324.9 |
898.6 |
1984 |
3,707.3 |
1,157.0 |
1,307.8 |
329.1 |
913.4 |
1985 |
4,167.1 |
1,414.6 |
1,442.0 |
363.3 |
947.2 |
1986 |
4,284.8 |
1,597.4 |
1,379.1 |
362.9 |
945.4 |
1987 |
6,876.3 |
2,503.4 |
2,322.5 |
863.6 |
1,186.8 |
1988 |
6,486.7 |
2,745.5 |
1,668.0 |
877.0 |
1,196.7 |
1989 |
8,759.5 |
3,629.9 |
2,363.6 |
1,256.7 |
1,509.3 |
1990 |
12,170.7 |
5,284.7 |
2,889.5 |
1,952.6 |
2,043.9 |
1991 |
13,113.7 |
5,248.6 |
3,309.5 |
2,308.9 |
2,246.7 |
1992 |
13,837.2 |
5,742.8 |
3,159.2 |
2,373.8 |
2,561.4 |
1993 |
13,729.3 |
6,421.2 |
2,450.8 |
2,317.6 |
2,539.9 |
1994 |
13,401.2 |
6,492.6 |
1,941.2 |
2,329.2 |
2,638.3 |
1995 |
14,172.9 |
7,226.9 |
1,819.2 |
2,247.4 |
2,879.2 |
1996 |
13,977.0 |
7,443.5 |
1,792.4 |
2,088.2 |
2,653.1 |
1997 |
15,267.4 |
7,804.1 |
2,329.9 |
2,334.3 |
2,799.1 |
1998 |
16,097.3 |
8,254.2 |
2,363.5 |
2,659.7 |
2,819.9 |
Dollars in Millions (unadjusted for inflation) |
|||||
1981 |
1,531.9 |
415.6 |
439.6 |
162.9 |
513.8 |
1982 |
1,718.9 |
475.3 |
571.4 |
166.6 |
505.6 |
1983 |
1,997.1 |
662.9 |
586.6 |
198.5 |
549.1 |
1984 |
2,363.1 |
737.5 |
833.6 |
209.8 |
582.2 |
1985 |
2,750.8 |
933.8 |
951.9 |
239.8 |
625.3 |
1986 |
2,881.1 |
1,074.1 |
927.3 |
244.0 |
635.7 |
1987 |
4,792.3 |
1,744.7 |
1,618.6 |
601.9 |
827.1 |
1988 |
4,707.8 |
1,992.6 |
1,210.2 |
636.5 |
868.5 |
1989 |
6,663.7 |
2,761.4 |
1,798.1 |
956.0 |
1,148.2 |
1990 |
9,758.9 |
4,237.5 |
2,316.9 |
1,565.7 |
1,638.9 |
1991 |
10,957.6 |
4,385.6 |
2,765.4 |
1,929.3 |
1,877.3 |
1992 |
11,910.1 |
4,943.0 |
2,719.2 |
2,043.2 |
2204.7 |
1993 |
12,171.1 |
5,692.4 |
2,172.6 |
2,054.6 |
2,251.6 |
1994 |
12,184.4 |
5,903.2 |
1,764.9 |
2,117.7 |
2,398.7 |
1995 |
13,251.2 |
6,756.9 |
1,700.9 |
2,101.3 |
2,692.0 |
1996 |
13,454.0 |
7,164.9 |
1,725.3 |
2,010.0 |
2,553.8 |
1997 |
15,033.2 |
7,684.4 |
2,294.2 |
2,298.5 |
2,756.2 |
1998 |
16,097.3 |
8,254.2 |
2,363.5 |
2,659.7 |
2,819.9 |
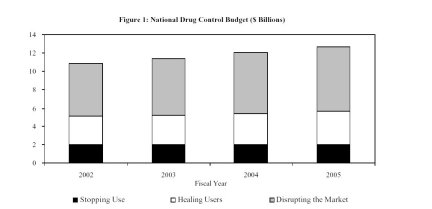
2005 Federal Anti-Drug Budget (executive summary)
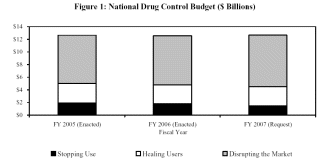
2007 Federal Anti-Drug Budget (executive summary)
2009--Change? (local copy)
- Profit (Jamaica-$1 billion, dealers: millions a month, POWER)
- Traditional enterprise in many lessor developed countries
- Issue of Imperialism and Neo-Colonialism
- Shift to domestic production
- Little land area is needed: Coca production needs less than 1000 square miles- 2,500,000 square miles available; Entire U.S. supply of heroin could be produce in only 50 square miles of opium fields (5% of opium production)
- If cultivation is controlled, still have the reality of synthetic production
- Heroin in Afghanistan: Enforcing drug laws versus a heroin-based economy?
Domestic Control
- DEA Statistics (arrests, Drug Seizures, and ER reports): http://www.usdoj.gov/dea/statisticsp.html
- Needle in a haystack
- Millions of boarder crossings
- Couriers/Mules: skills and replaceable
- Hit one, another pops up
- NYC: est. 250,000 earn living off of illicit drugs
- 1982: $200 million seized. 1990: Over $1 billion (10 tons of cocaine)seized- still readily available
- Drug Asset Forfeiture (1988 Anti-Drug Abuse Bill)
- Miller and Selva (1994, disguised observation, Goode: page 394)
- "Law of unanticipated consequences": Asset hunting versus policing.
- Organizational versus personal corruption (narcotic officiers as revenue hunters).
- Vecci and Sigle (2001, interviews, Goode page 395)
- Officers think: effective
- Officers rank as important
- Local versus federal agency: dependence on forfeiture monies.
- Proactive Policing
- Zimmer (1990, Goode pages 396-397): "Operation Pressure Point" in Manhatten, late 1980s
- Overall: Decline in outside traffic and drug related crime
- Decline versus eliminated
- Diversion--shift activity to other neighborhoods
- Differential impact based on SES: block by block effect
Increase Penalties
- Law of Criminal Justice Thermodynamics: The more severe the penalty, the less likely is the application: 1973 NY law- very harsh penalties: use rises (general trend) and arrests remain stable
- Prison costs and overcrowding
- CJS inundation: Crime down, Use level: Arrests for drug related offenses up.
- Inmates are categorized based on their most serious offense. As of January 23, 1998, 15% (3614) inmates in the Missouri Prison system (this does exclude those in jails) where incarcerated with their most serious offense being a drug offense. (from a telephone conversation with officials of the Missouri Department of Corrections 2/10/98)
- Over 400,000 arrests in 1994 for marijuana
- In some jurisdictions: 50% of inmate population
- Expanding the net: How much are we willing to give up?
- County by county arrests in Missouri: Marijuana Arrests By Rate 1995 - 1997
(Source: FBI, The Uniform Crime Reports (UCR) and http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/glance/drug.htm)
- 2002: Cost of "War on Marijuana."
- 2003 Marijuana Arrests
- War on Drugs Shifts to War on Marijuana ("A study of FBI arrest and conviction data by a Washington think-tank has underscored a dramatic shift in US drug policy in the decade of the 1990s. "The War on Marijuana: The Transformation of the War on Drugs,", released Tuesday by the Sentencing Project, reports that from 1992 to 2002, the proportion of drug arrests involving marijuana increased from 28% to 45% of all drug arrests, while arrests for the much more dangerous cocaine and heroin decreased from more than half of all drug arrests to less than 30%. " http://stopthedrugwar.org/chronicle/385/shifted.shtml 5/6/05))
Does Prohibition Work?
- MacCoun and Reuter (2001): no significant link between severity or certainty and drug involvement (Goode, pages 397-398).
- Multinational embeddedness
- Since 1981 (beginning of "war): cocaine and heroin prices down and purity up (Rhoades, Johnston, and King, 2001, in Goode page 399).
- Absolute versus relative deterrence
- Efficacy.org (http://www.efficacy-online.org/) A focus on the problems with the "war on drugs."
- Drugsense Drug War Clock: http://www.drugsense.org/wodclock.htm
- The Failure of Drug Control Policies, Gary Potter, Criminal Justice and Police Studies, Eastern Kentucky University
- Race, Arrest, and Incarceration and the drug war on minorities.
Legalization
- Entails regulation and potential tax revenues
- State's role in distribution and oversight
- Illicit Drug Trade Sources: http://www.princeton.edu/~ina/drugs/sources.html
- Drug Use in Europe
Decriminalization
- Full versus partial decriminalization
- Misdemeanor vs. Felony- removal of criminal penalties
- Distinguishes between use, possession, and distribution
- Basically asserts the State no longer has a significant role or interest in the regulation of the activity.
- Decriminalization in Latin America (2009)
Maintenance/Prescription Drug Model
- Treatment of drug dependency
- Use of heroin and heroin maintenance
- Goode on Heroin Maintenance in the USA (1999)
- Problem of leakage
- Screening and admission policies
- Stabilization problems: Euphoria seekers vs. Maintainers
- Assume all addicts would enroll?
- Only source of medicinal heroin?
- Medicalization
Legalization/Decriminalization Arguments
see also: Between Politics and Reason- The Drug Legalization Debate, Erich Goode, 1997.
- Use would not rise much
- Apollonian versus Dionysian Culture (fear mongering and reality: proportionality
- Extensive availability already
- Yet:
- Alcohol use did decline during Prohibition
- Availability of drugs in Viet Nam- high rates of use (yet circumstances different)
- High rates of use in medical profession (easy availability)
- Legal drugs have high rates of use, and use is stable
- So, yes there would most likely be an increase. It that necessarily a problem? Depends on the drug!
- Nonetheless, demand does exist (and profit, too)
- Drug effects and social context
- Harm produced by drugs themselves is not so significant
- Current policies do not work. Waste of people and resources. Criminalization does not deter use.
- Punitive strategy:
- Push down -- Pop up
- Increases profit
- Stimulates that which it seeks to control (crime)
- Produces unregulated, uncontrolled and contaminated market
- Produces a shift to more potent drugs ("Iron Law of Prohibition"): smuggling and profit; paraquat; Jake during Prohibition, etc.
- Cost of interdiction and enforcement: Over $20 billion a year- If legalized the State could make money!
- Ethan Nadelmann on Drug Prohibition in the USA: http://www.lindesmith.org/docUploads/Colliers_encyclo.pdf (1995 Collier’s Encyclopedia’s)
- Impedes access to therapeutic substances
- Political and Moral Issues
- Privacy and civil rights
- Police corruption
- Criminalization of an entire category of people
- Stimulates disrespect for the law
European Model: Harm Reduction
- Harm reduction (another view) (and Public Health)
- Europe leading the way to smarter drug laws Part One and Part Two, by Dan Gardner (The Ottawa Citizen, Friday 15 September 2000)
- Practical use of resources
- Flexible enforcement practices
- Tolerance rather than approval
- Education/prevention and treatment versus incarceration
- Expand maintenance
- Demarginalize populations
- Cannabis: a harm reduction perspective. Chapter 11 of A cannabis reader: global issues and local experiences, EMCDDA, Lisbon, June 2008 (local copy in .pdf).
- International Harm Reduction: Harm Reduction in Europe: Mapping Coverage and Civil Society Advocacy 2011 (local copy)
Recent research from CEDRO
The origins and future of the Dutch approach towards drugs
by Justus UitermarkThis paper considers the roots of the Dutch approach towards drugs. It argues that the idiosyncratic nature of Dutch drug policies can be explained by taking into account the peculiar evolution of the Netherlands ’ political institutions. The distinctive character of Dutch policies is explained through the concept of gedogen. Gedogen refers to the practice of discriminatory enforcement. Gedogen can be defined as a regulatory system of organized toleration and targeted repression. Only those illegalities that are actually considered to cause social problems are targeted for repression. As such, the policy differs markedly from orthodox prohibitionist policy approaches. Policies towards ecstasy and cannabis are discussed to illustrate how gedogen works in practice. While it is argued that gedogen has functioned well for a number of years, doubts are expressed about the extent to which the Netherlands can be expected to continue to play the role of pioneer with respect to drug policies. After a revival of conservative politics, the country now seems ill equipped to develop alternative drug policies.
<http://www.cedro-uva.org/lib/uitermark.origins.html>
Decriminalize Marijuana?
- Erroneous belief that use can be eliminated
- Decline in use, and current rise seem to be products of the sub-culture rather than legal policies
- Arrests don't seem to impact use (when high, use is high; when low, use is low)
- Health consequences seem negligible
- Medicinal use
- Practically true, anyway
Heroin and Cocaine: Special Problems?
- Not as available as "soft" drugs
- Sensuous appeal
- Dependency and frequent use
- Issue of crime and disease
- Apollonian/Dionysian Culture again. Which are we?
- Most use non-abusively, but prediction is that absolute number of abuser will rise: dramatic impact.
Practical Issues of Legalization
Containment and Harm reduction (another view) (and Public Health)
Potential for success?
Varied Political Ideologies (Public Agenda: Illegal Drugs Discussion Guide)
(from Goode, 2005, page 442)
Drugs are a Part of Life
The solution to the "drug problem" is not "drug free."
- Controlled use
- Reduction of risk and harm reduction: Treatment and beyond (Drug Policy Alliance)
- Economic and social stability: Demarginalization
Reasonable suggestions?
- Decriminalize marijuana expand access for medicinal use.
- No arrests for simple possession of so-called hard drugs.
- Non-penal approach to low level dealing and distribution.
- No prison: Focus on demand reduction (currently only 1/4 of the budget goes toward prevention/treatment).
- Expand treatment availability.
- Leave other countries alone
- Reschedule: explore therapeutic use of LSD, ecstasy, heroin.
- Refocus on alcohol and tobacco.
Quit Dreaming of a Drug Free America!
What do YOU think?
![]()
URL: http://www.umsl.edu/~keelr/180/policy.html
Owner: Robert O. Keel rok@umsl.edu
References and
Credits for this Page of Notes
Last Updated:
Tuesday, December 27, 2011 7:59 AM